
This week is American Education Week, a time in which we celebrate public education and educators. The National Center for Special Education Research supports educators and service providers of learners with and at risk for disabilities through funding rigorous research in this area. The NCSER grant program Educators and School-Based Service Providers strives to improve outcomes for students with or at risk for disabilities by finding effective strategies for pre-service teacher preparation and in-service teacher professional development to close the research-to-practice gap.
NCSER awarded three new research grants in FY 2020 through the Educators and School-Based Service Providers program:
Addressing Emergency Certification in Rural Education Settings (Project ACRES)
The purpose of this project is to develop and test a professional development program for emergency certified special educators in rural school districts. There is a nationwide shortage of special educators and this shortage tends to be greater in rural locations. Emergency certification exists to fill the gap by providing provisional licensure to educators while they work towards formal certification. Novice special educators frequently rank behavior management as a top concern, and this area is likely an even greater challenge for teachers with emergency credentials. Kimber Wilkerson and her colleagues will develop a professional development program and test its promise for improving emergency certified special educators’ behavior management skills, self-efficacy, and likelihood of remaining in the field. They will also examine the promise of the program for improving students’ behavior outcomes.
Build the FRaME: Using Feedback, Reflection, and Multimedia to Teach Evidence-Based Practices for Effective Classroom Management
In this study researchers will develop and test a multimedia, multicomponent instructional approach to be used within teacher preparation programs. Teachers nationwide report feeling underprepared to manage classrooms that include students with disabilities and students who exhibit challenging behavior. Michael Kennedy and his team are designing an instructional approach, FRaME, that will improve teacher candidate knowledge and implementation of evidence-based classroom management practices and the engagement and achievement of K-12 learners with disabilities.
Developing an Instructional Leader Adaptive Intervention Model (AIM) for Supporting Teachers as They Integrate Evidence-Based Adolescent Literacy Practices School-Wide (Project AIM)
This project will develop and test a comprehensive intervention model that includes adaptive, multistage coaching for middle school teachers delivering Tier 1 evidence-based literacy instruction and professional development for school-based coaches. While evidence-based literacy practices have the potential to impact reading outcomes for students with disabilities, teachers do not always implement these practices with consistency or fidelity. Jade Wexler and her team will develop this model and examine its promise for improving teachers’ knowledge of evidence-based literacy practices and students’ reading outcomes. They will also examine the program’s sustainability.
The ultimate goal of IES is to improve opportunities and outcomes for all learners. Research on professional development and teacher preparation is one way to support the provision of high-quality education for all students within the public education system, including those with or at risk for disabilities.
This blog was authored by Alice Bravo (University of Washington), IES intern through the Virtual Student Federal Service. For more information about NCSER’s Educators and School-Based Service Providers program, contact Dr. Katie Taylor.
In 1921, the National Education Association (NEA) sponsored the first American Education Week to express gratitude for U.S. public school educators who work hard every day to ensure all students receive a quality education. To celebrate education professionals working in the more than 98,000 U.S. public schools during this year’s American Education Week, NCES will share facts and figures from the National Teacher and Principal Survey (NTPS) in two blogs (read part 2 here).
The NTPS is a great resource for educators looking to better understand the characteristics and experiences of their professional communities both nationally and by state (using the NTPS State Dashboard). The NTPS collects information about school conditions and the demographics of public and private school teachers and principals, providing data that policymakers and researchers use to inform funding and other decisions.
In honor of American Education Week, here are some selected facts and figures about U.S. public schools from the NTPS (note that these data were collected prior to the coronavirus pandemic).
AEW Day 1: U.S. Public Schools (2017–18 NTPS)
- The majority of elementary teachers teach in self-contained classrooms (i.e., they instruct the same group of students all or most of the day), while the majority of middle and high school teachers teach in departmentalized classrooms (i.e., they teach several classes of different students all or most of the day in different subjects).[1]
- The average class size for teachers in self-contained classrooms in primary schools was 21 students (figure 1).
- The average class size for teachers in departmentalized classrooms in middle schools was 25 students, which was higher than the average class size for teachers in departmentalized classrooms in high schools (23 students).
Figure 1. Average class size in U.S. public schools, by class type and school level: 2017–18
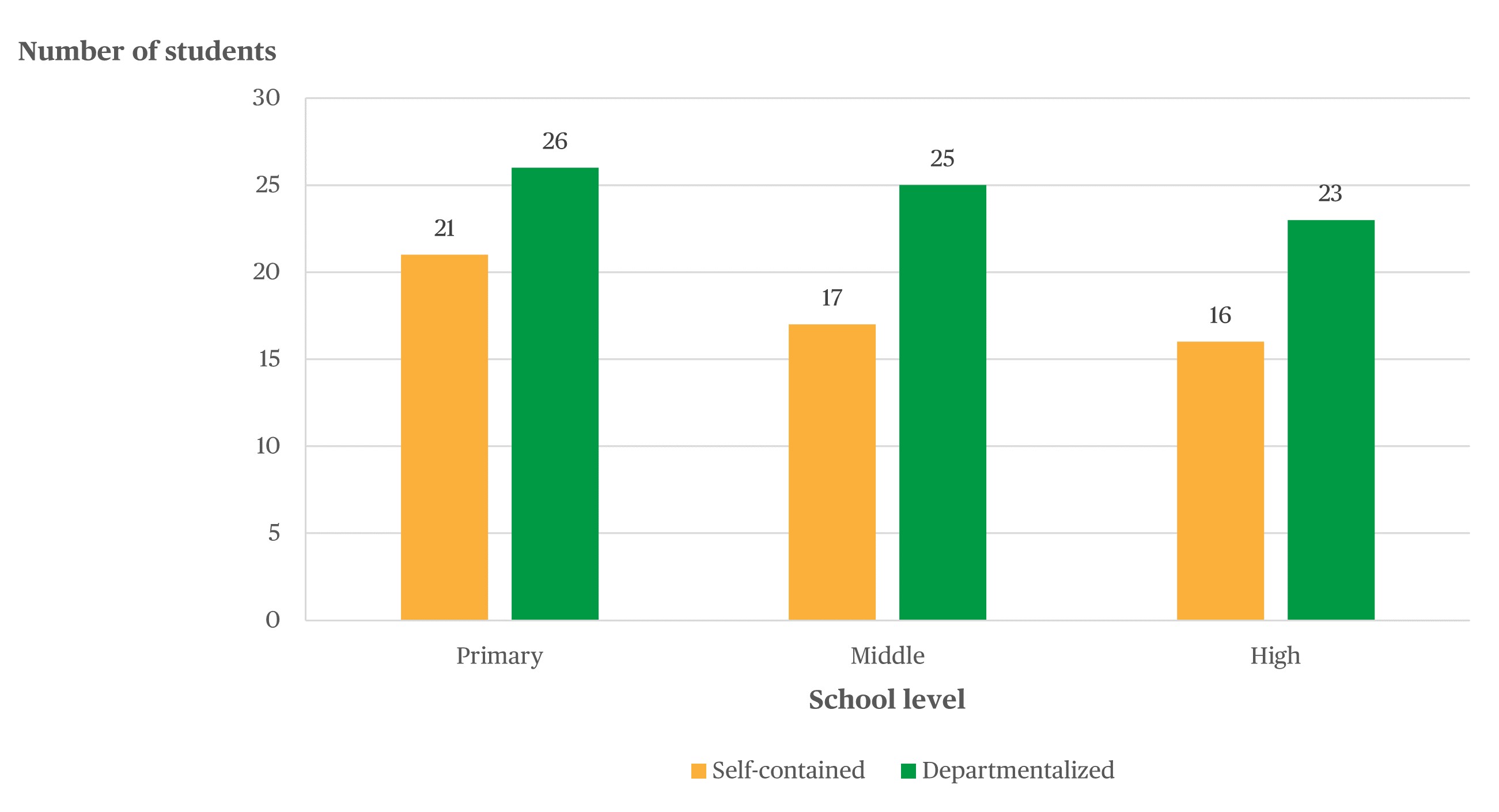
NOTE: Self-contained classes are defined as instruction to the same group of students all or most of the day in multiple subjects. Departmentalized instruction is defined as instruction to several classes of different students most or all of the day in one or more subjects. Among all public school teachers, 25 percent teach self-contained classes in primary schools, 1 percent do so in middle schools, and 1 percent do so in high schools; 8 percent teach departmentalized classes in primary schools, 14 percent do so in middle schools, and 24 do so percent in high schools; and 15 percent teach other types of classes, such as elementary subject specialist classes, team-taught classes, and "pull-out" or "push-in" classes in primary schools, 3 percent do so in middle schools, and 3 percent do so in high schools.
SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, National Teacher and Principal Survey (NTPS), "Public School Teacher Data File," 2017–18.
AEW Day 2: Parent Involvement in U.S. Public Schools (2017–18 NTPS)
The National Parent Teacher Association reports that “the most accurate predictors of student achievement in school are not family income or social status, but the extent to which the family . . . becomes involved in the child’s education at school.”[2]
- Most U.S. public schools offered at least one opportunity for parents and/or guardians to participate in an event or activity at their child’s school, such as parent-teacher conferences and back-to-school nights.
- Among principals in schools that offered various opportunities for parent participation, the percentages of primary school principals who reported that 76–100 percent of parents attended an engagement opportunity were higher than the percentages of middle and high school principals for most opportunities (figure 2).
- More parents of primary school students than parents of middle and high school students attended open house or back-to-school night events, parent-teacher conferences, subject-area events,[3] and parent education workshop courses; volunteered in the school; and signed a school-parent compact.[4]
Figure 2. Percentage of principals in schools that offered various opportunities for parent participation who reported that 76–100 percent of parents participated in different opportunities, by opportunity type and school level: 2017–18
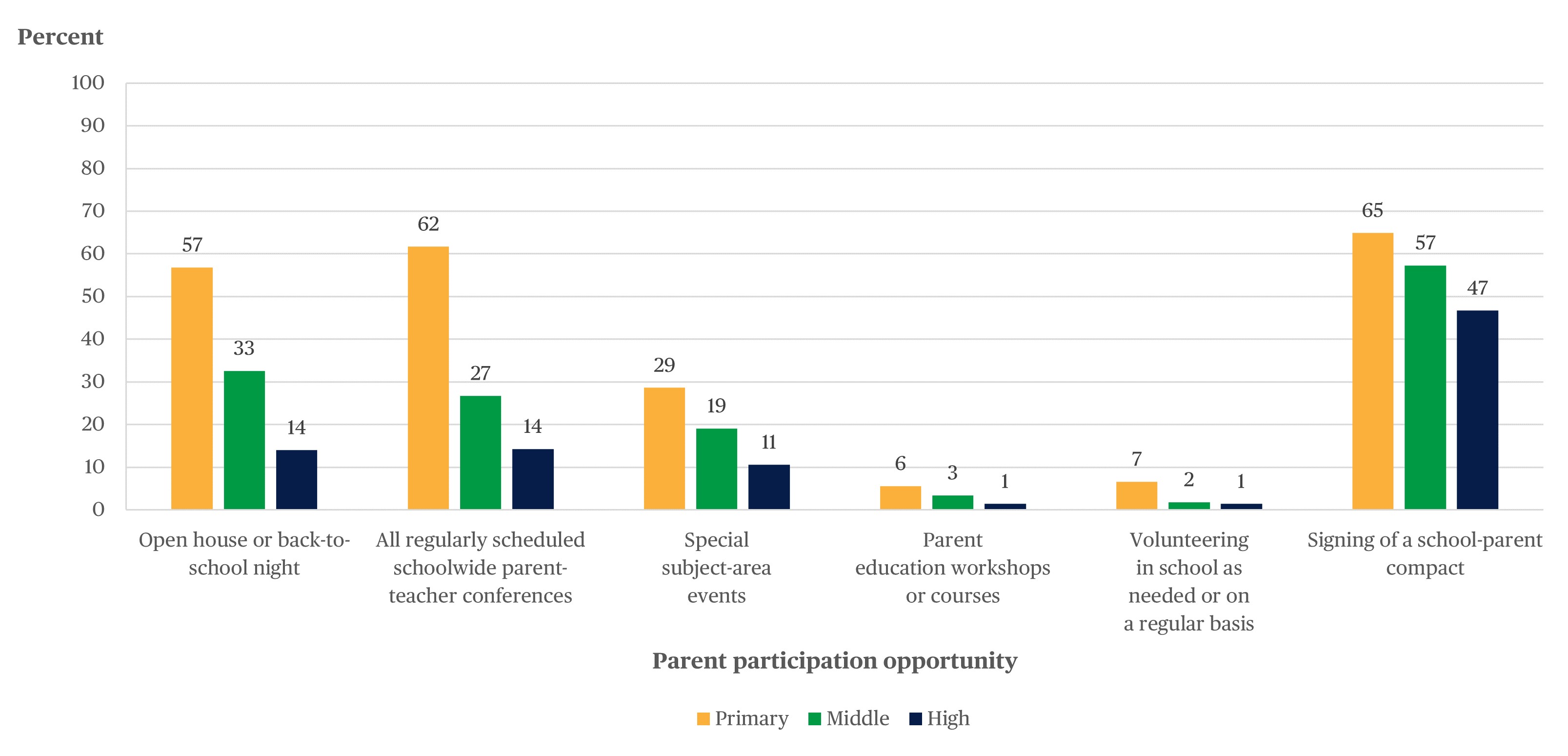 ! Interpret data with caution. The coefficient of variation (CV) for this estimate is between 30 and 50 percent.
! Interpret data with caution. The coefficient of variation (CV) for this estimate is between 30 and 50 percent.
SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, National Teacher and Principal Survey (NTPS), "Public School Teacher Data File," 2017–18.
AEW Day 3: Education Support Professionals in U.S. Public Schools (2015–16 NTPS)
Education support professionals are nonteaching staff, including nurses, librarians, and student support services professionals (such as school counselors, psychologists, social workers) whose contributions keep schools organized and help students stay safe, healthy, and ready to learn.
- Ninety-four percent of all public schools had at least one full- or part-time counselor, psychologist, or social worker; the percentage of schools that had at least one full- or part-time counselor (81 percent) was greater than the percentages that had at least one full- or part-time psychologist (67 percent) and social worker (42 percent). Six percent had neither a counselor, psychologist, nor social worker on staff.
- High poverty schools—schools where 75 percent or more of students were approved for the free or reduced-price lunch (FRPL) program—had fewer education support professionals on staff than did schools with lower FRPL participation rates (0–34 percent, 35–49 percent, and 50–74 percent).
- Eight percent of high-poverty schools had neither a counselor, psychologist, nor social worker on staff, compared with 3 percent of schools with 0–34 percent or with 35–49 percent FRPL participation.
Next, in part 2 of the NTPS blog series for American Education Week, we will share facts and findings about educators.
In honor of American Education Week, NCES would like to thank every parent and/or guardian, education support professional, educator, and principal who makes public education possible for students every day!
The data in this blog would not be possible without the participation of teachers, principals, and school staff in the NTPS. We are currently conducting the 2020–21 NTPS to learn more about teaching experiences during the pandemic. If you were contacted about participating in the 2020–21 NTPS and have questions, please email ntps@census.gov or call 1-888-595-1338.
For more information about the National Teacher and Principal Survey (NTPS), please visit https://nces.ed.gov/surveys/ntps/. More findings and details are available in the NTPS school, teacher, and principal reports.
By Julia Merlin, NCES
[1] There may be meaningful differences within the student body at middle and high schools that offer self-contained classrooms that differ from the characteristics of those students in self-contained classrooms at primary schools.
[2] National PTA. 2000. Building Successful Partnerships: A Guide for Developing Parent and Family Involvement Programs. Bloomington, Indiana: National Education Service, 11–12.
[3] Special subject-area events include events such as science fairs and concerts.
[4] A school-parent compact is an agreement between school community members (e.g., parents, principals, teachers, students) that acknowledges the shared responsibility for students learning and/or the school's policies.