Although traditional pencil and paper tests provide good information for many purposes, technology presents the opportunity to assess students on tasks that better elicit the real world skills called for by college and career standards. IES supports a number of researchers and developers who are using technology to develop better assessments through grants as well as the Small Business Innovation Research program.
 One example of the power of technology to support innovative assessment is the Global, Integrated, Scenario-based Assessment (known as ‘GISA’), developed by John Sabatini and Tenaha O’Reilly at the Educational Testing Service as part of a grant supported by the Reading for Understanding Research Initiative.
One example of the power of technology to support innovative assessment is the Global, Integrated, Scenario-based Assessment (known as ‘GISA’), developed by John Sabatini and Tenaha O’Reilly at the Educational Testing Service as part of a grant supported by the Reading for Understanding Research Initiative.
Each GISA scenario is structured to resemble a timely, real-world situation. For example, one scenario begins by explaining that the class has been asked to create a website on green schools. The student is assigned the task of working with several students (represented by computer avatars) to create the website. In working through the scenario, the student engages in activities that are scaffolded to support students in summarizing information, completing a graphic organizer, and collaborating to evaluate whether statements are facts or opinions. The scenario provides a measure of each student’s ability to learn from text through assessing his or her knowledge of green schools before and after completing the scenario. This scenario is available on the ETS website along with more information about the principles on which GISA was built.
Karen Douglas, of the National Center for Education Research, recently spoke to Dr. Sabatini and Dr. O’Reilly on the role of technology in creating GISA, what users think of it, and their plans for continuing to develop technology-based assessments.
How did the use of technology contribute to the design of GISA?
Technological delivery creates many opportunities over more traditional paper and pencil test designs. On the efficiency side of the argument, items and tasks can be delivered over the internet in a standardized way and there are obvious advantages for automated scoring. However, the real advantage has to do with both the control over test environment and what can be assessed. We can more effectively simulate the digital environments that students use in school, leisure and, later, in the workforce. GISA uses scenario-based assessment to deliver items and tasks. During a scenario-based assessment students are given a plausible reason for reading a collection of thematically related materials. The purpose defines what is important to focus on as students work towards a larger goal. The materials are diverse and may reflect different perspectives and quality of information.
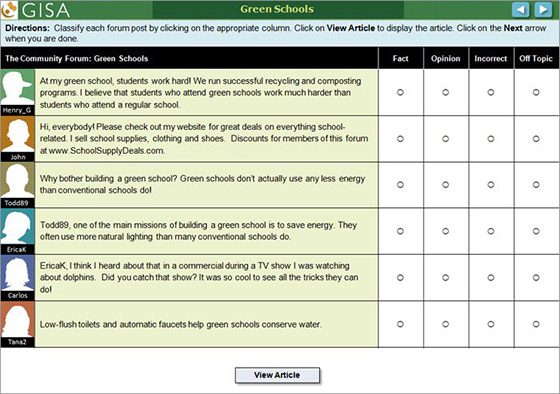
The student not only needs to understand these materials but also needs to evaluate and integrate them as they solve problems, make decisions, or apply what they learn to new situations. This design is not only more like the activities that occur in school, but also affords the opportunity for engaging students in deeper thinking. GISA also includes simulated students that may support or scaffold the test taker's understanding with good habits of mind such as the use of reading strategies. Items are sequenced to build up test takers’ understanding and to examine what parts of a more complex task students can or cannot do. In this way, the assessment serves as a model for learning while simultaneously assessing reading. Traditionally, the areas of instruction and assessment have not been integrated in a seamless manner.
What evidence do you have that GISA provides useful information about reading skills?
We have a lot more research to conduct, but thus far we have been able to create a new technology- delivered assessment that updates the aspects of reading that are measured and introduces a variety of new features.
Despite the novel interface, items, tasks, and format, students are able to understand what is expected of them. Our analyses indicate the test properties are good and that students can do a range of tasks that were previously untested in traditional assessments. While students may be developing their skills on more complex tasks, there is evidence they can do many of the components that feed into it. In this way the assessment may be more instructionally relevant.
Informally, we have received positive feedback on GISA from both teachers and students. Teachers view the assessment as better matching the types of activities they teach in the classroom, while students seem to enjoy the more realistic purpose for reading, the more relevant materials, and the use of simulated peers.
What role do you think technology will play in future efforts to create better assessments?
We believe technology will play a greater role in how assessments are designed and delivered. Being able to provide feedback to students and better match the test to student needs are some areas where future assessments will drive innovation. More interactive formats, such as intelligent tutoring and gaming, will also grow over time. With new forms of technology available, the possibilities for meeting students’ educational needs increases dramatically.
What’s next for GISA?
We are using GISA in two additional grants. In one grant, we leverage the GISA designs for use with adults, a group for which there are few viable assessments. In the other grant we are using GISA to get a better understanding of how background knowledge affects reading comprehension.
For more information about the Reading for Understanding Research Initiative, read this post on the IES blog.
By Karen Douglas, Education Research Analyst, NCER, who oversees the Reading for Understanding Research Initiative