Policymakers, researchers, and the public have long voiced concerns about the equitable distribution of school funding within and across school districts. More recently, the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) requires that states and school districts add per pupil expenditures, disaggregated by source of funds, to their annual report cards for each local education agency (LEA) (e.g., school district) and school. In response to this these requirements, the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) developed a new collection of finance data at the school level—the School-Level Finance Survey (SLFS).
The SLFS collects at the school level many of the same expenditure variables currently being collected at the district level on the School District Finance Survey. The pilot SLFS was designed to evaluate whether the survey is a viable, efficient, and cost-effective method to gather school-level finance data. Findings from the pilot survey were recently released in an NCES report titled The Feasibility of Collecting School-Level Finance Data: An Evaluation of Data From the School-Level Finance Survey (SLFS) School Year 2014–15.
Here’s some of what we learned:
Many states participating in the SLFS were able to report complete personnel and/or nonpersonnel expenditure data for a high percentage of their schools.
Of the 15 states that participated in the SLFS in school year 2014–15, 9 states were able to report school-level finance data for greater than 95 percent of their operational schools (figure 1). Other than Colorado and New Jersey,[1] all states were able to report SLFS data for at least 84 percent of their schools, ranging from 85 percent in Kentucky to nearly 100 percent in Maine. Just over one-half of reporting states (8 of 15) reported all personnel items (i.e., dollars spent on salaries and wages for teachers, aides, administrators, and support staff) for at least 95 percent of their schools. Seven of 15 states reported all nonpersonnel items (i.e., dollars spent on purchased services, supplies, and other costs not directly related to school employees) for at least 95 percent of their schools.
Figure 1. Percentage of operational schools with fiscal data reported in the SLFS, by participating state: 2014–15
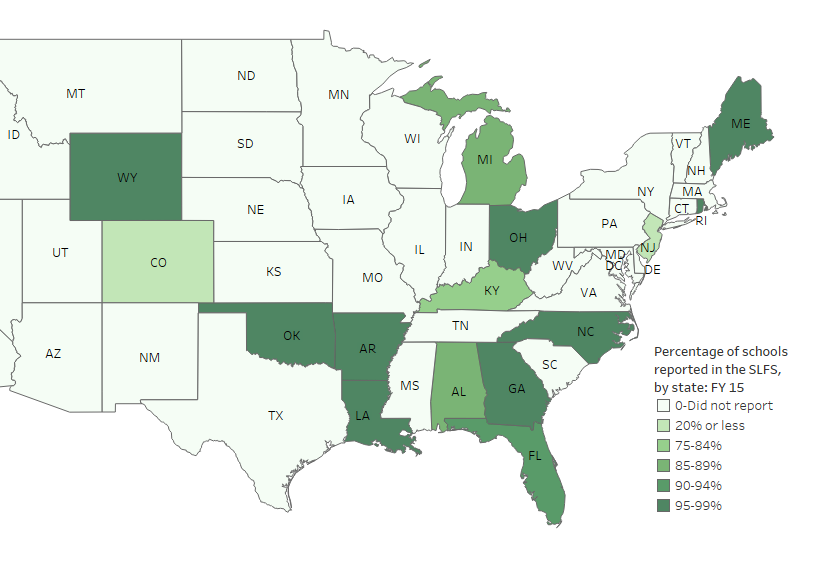
NOTE: This figure includes operational schools only (i.e., excludes closed, inactive, or future LEAs). The count of schools reported includes schools that can be matched to the Common Core of Data (CCD) School Universe files and for which at least one data item is reported in the SLFS.
SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, Common Core of Data (CCD), “School-Level Finance Survey (SLFS),” fiscal year 2015, Preliminary Version 1a; “Local Education Agency Universe Survey,” 2014–15, Provisional Version 1a.
SLFS data are generally comparable and consistent with other sources of school finance data.
A substantial majority of personnel expenditures can be reported at the school level. Personnel expenditures reported for the SLFS were reasonably comparable with the district-level and state-level data.[2] For common personnel expenditures, the absolute percentage difference between the SLFS and the district survey was less than 9 percent in 8 of 10 states (figure 2). The absolute percentage difference between the SLFS and the state-level survey for common personnel expenditures was less than 9 percent in 6 of 10 states.
Figure 2. School-Level Finance Survey (SLFS), School District Finance Survey (F-33), and National Public Education Financial Survey (NPEFS), by participating state: 2014–15
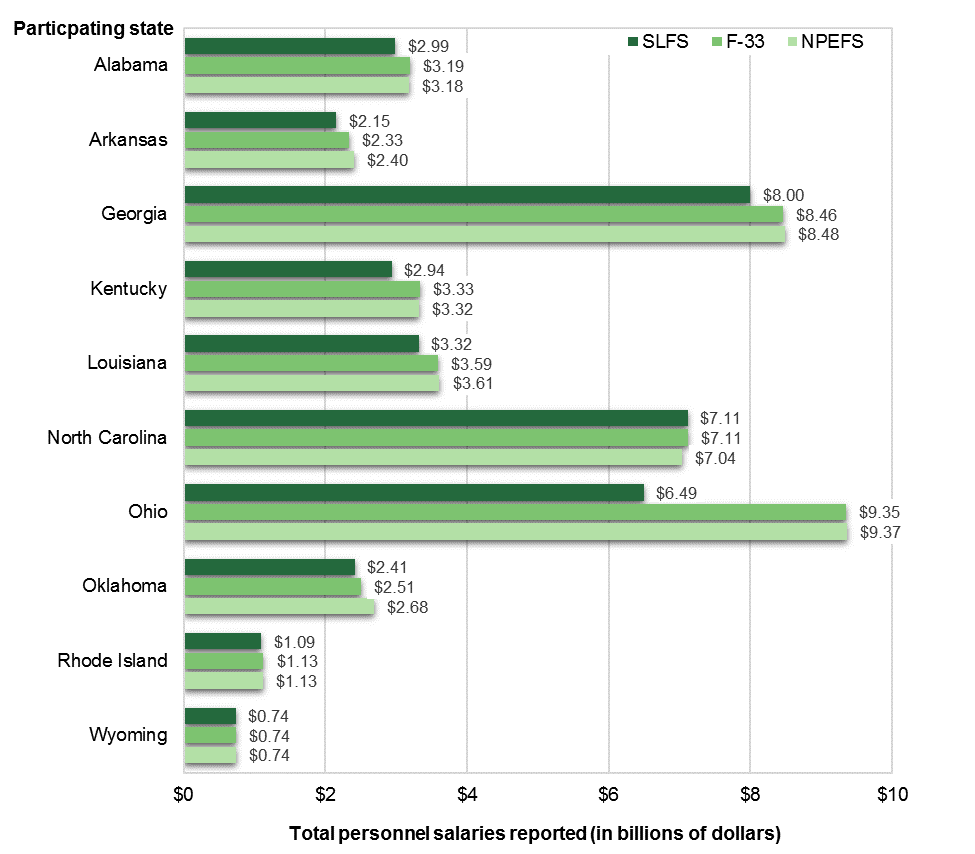
NOTE: Total personnel salaries include instructional staff salaries, student support services salaries, instructional staff support services salaries, and school administration salaries. This figure includes all schools in the SLFS and all LEAs in the F-33. Only states where reporting standards are met are included.
SOURCE: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, Common Core of Data (CCD), “School-Level Finance Survey (SLFS),” fiscal year 2015, Preliminary Version 1a; “National Public Education Financial Survey (NPEFS),” fiscal year 2015, Final Version 2a; and “School District Finance Survey (F-33),” fiscal year 2015, Provisional Version 1a.
There are numerous inherent challenges in collecting school-level finance data:
- Communicating the vision of why reporting school-level finance data is important to school finance practitioners.
- The pilot SLFS did not collect all types of current expenditures.
- Some states had not fully developed standardized protocols or procedures for reporting finance data at the school level.
- There are varying legal requirements for the types of schools that are required to report finance data and the types of expenditures schools and districts are required to report.
- The survey’s data item definitions were not consistent with states’ internal accounting for some items.
During the pilot survey, NCES and Census Bureau staff took action to address these challenges.
Evidence suggests that it is feasible to collect accurate and informative school-level financial data.
States participating in the SLFS are improving internal data systems and protocols, which will allow them to report complete and comparable school-level finance data. The SLFS promotes efficiency by incorporating long-established NCES standards for school district financial accounting. The results of the pilot SLFS survey demonstrate that it is feasible to collect accurate and informative school-level finance data. The informational and analytical value will increase as response rates improve and as states improve their capabilities to collect complete, accurate, and comparable finance data at the school level.
By Stephen Q. Cornman, NCES; Malia Howell, Stephen Wheeler, and Osei Ampadu, U.S. Census Bureau; and Lei Zhou, Activate Research
[1] In 2014–15, Colorado did not require all school districts to report finance data at the school level; thus, data is reported for only 26 of Colorado’s 262 LEAs. In New Jersey, school-level finance reporting is required only for its “Abbott” districts, which make up only 31 of the state’s 702 districts.
[2] NCES’s Common Core of Data (CCD) program collects school finance data through three annual surveys: the school-level SLFS, the LEA-level School District Finance Survey (F-33), and the state-level National Public Education Financial Survey (NPEFS). Five data items are common to all three fiscal surveys (i.e., are collected at the school level for the SLFS, at the LEA level for the F-33, and at the state level for the NPEFS): instructional staff salaries, student support services salaries, instructional staff support services salaries, school administration salaries, and teacher salaries.