Recognizing the extraordinary information needs of policymakers during the coronavirus pandemic, NCES joined a partnership with the Census Bureau and four other federal statistical agencies to quickly develop a survey to gather key indicators of our nation’s response to the global pandemic. Thus, the experimental 2020 Household Pulse Survey began development on March 23, 2020, and data collection began on April 23, 2020. This new survey provides weekly national and state estimates, which are released to the public in tabular formats one week after the end of data collection.
The Household Pulse Survey gathers information from adults about employment status, spending patterns, food security, housing, physical and mental health, access to health care, and educational disruption. The education component includes questions about the following:
- The weekly time spent on educational activities by students in public and private elementary and secondary schools
- The availability of computer equipment and the Internet for instructional purposes
- The extent to which computer equipment and the Internet for students were provided or subsidized
Since this survey is designed to represent adults 18 years old and over, the responses to the education questions concern students within the households of adults 18 years old and over, not the percentage of students themselves.
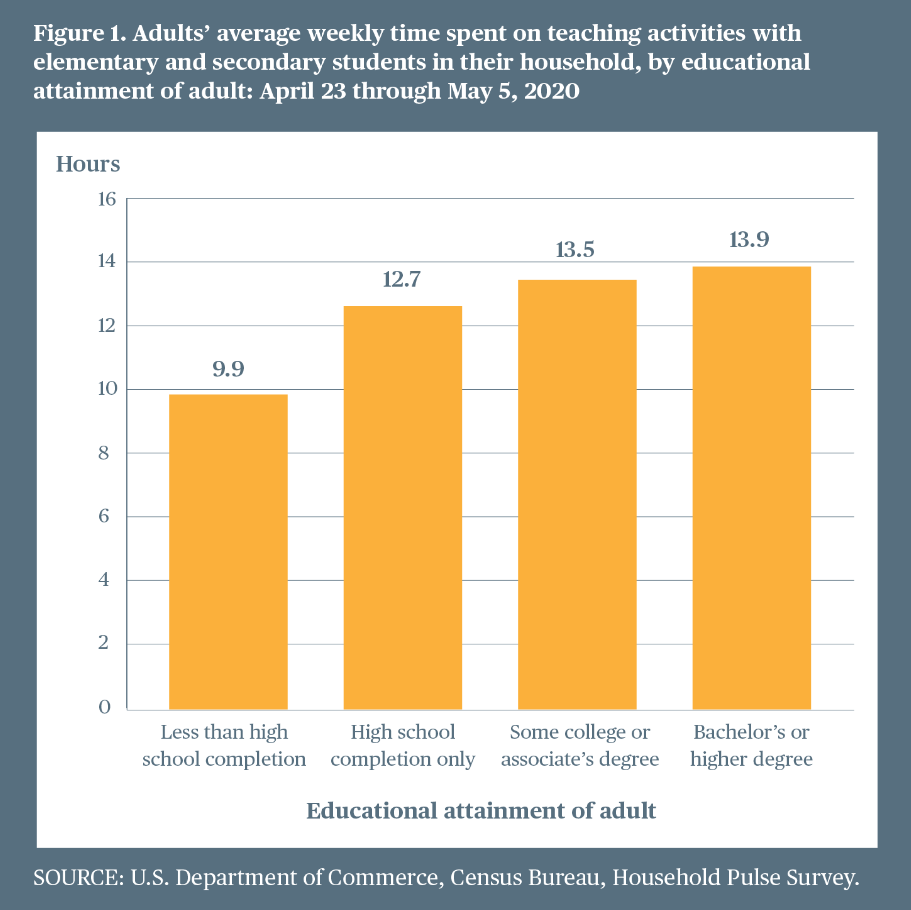
In the Household Pulse Survey during the weeks of April 23 through May 5, adults reported that their average weekly time spent on teaching activities with elementary and secondary students in their household was 13.1 hours. These results differed by educational attainment: adults who had not completed high school reported a weekly average of 9.9 hours in teaching activities with children, whereas adults with a bachelor’s or higher degree reported 13.9 hours (figure 1). In terms of the average weekly time spent on live virtual contact between students in their household and their teachers, adults reported a lower average of 4.1 hours.
Adults’ reports about the school instruction model need to be interpreted carefully because respondents could choose multiple types of approaches. A higher percentage of adults with a bachelor’s or higher degree (84 percent) reported that classes for elementary and secondary students in their household had moved to a format using online resources than did adults who had completed some college or an associate’s degree (74 percent), adults who had completed only high school (64 percent), or adults who had not completed high school (57 percent).
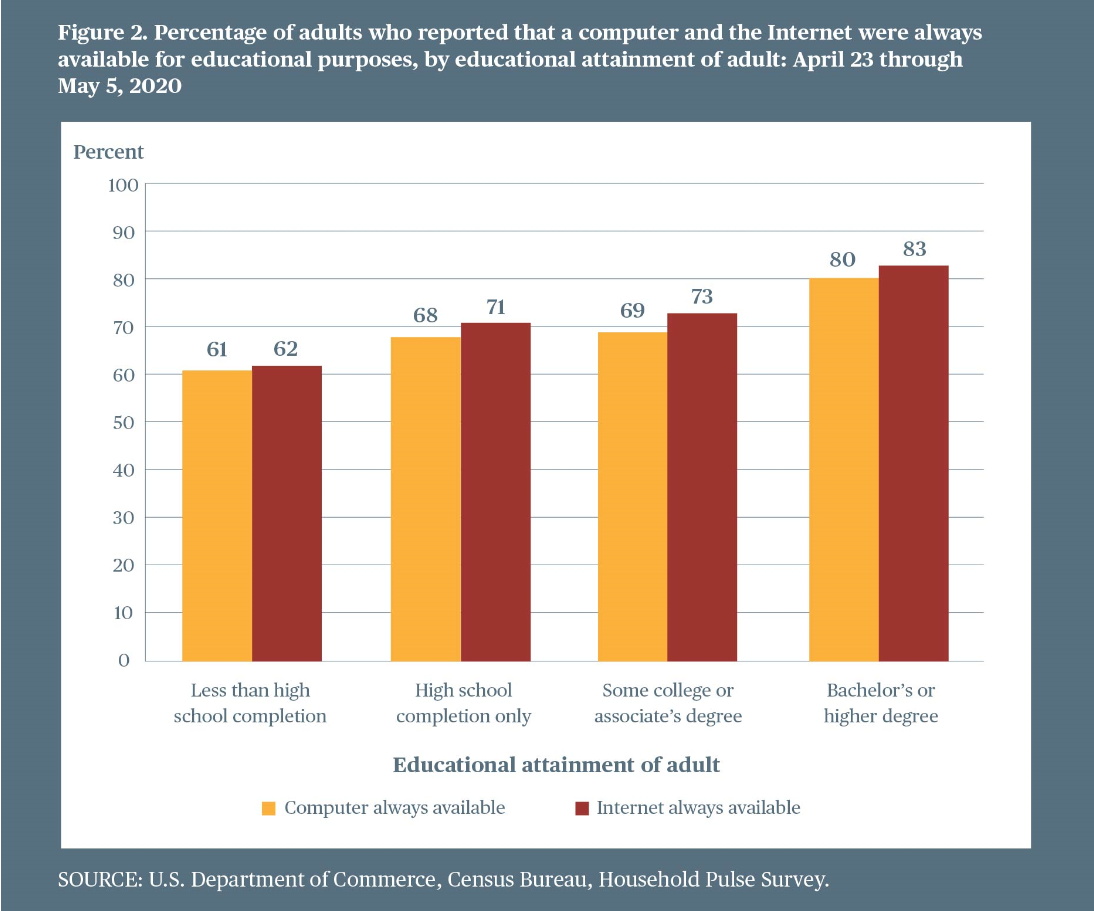
Higher percentages of adults with higher levels of education than of adults with lower levels of education reported that computers and the Internet were always available for educational purposes for elementary and secondary students in their households (figure 2).
The percentage of adults who reported that the school district provided a computer or digital device for children in their households to use at home for educational purposes was higher for adults who had not completed high school (44 percent) than for adults with a bachelor’s or higher degree (33 percent). Also, a higher percentage of adults who had not completed high school than of adults with higher levels of educational attainment reported financial assistance for student Internet access.
It is important to note that the speed of the survey development and the pace of the data collection efforts have led to policies and procedures for the experimental Household Pulse Survey that are not always consistent with traditional federal survey operations. Data should be interpreted with proper caution.
More information on the Household Pulse Survey, detailed statistical tables, and microdata sets are available at https://www.census.gov/householdpulsedata. The Household Pulse Survey site includes breakouts of the data by other characteristics, such as race/ethnicity. In addition to participating in the development of this new survey, NCES has also generated new analyses based on existing data that respond to new needs for policy information, such as the availability of the Internet for student learning.
By Xiaolei Wang, AIR