International comparisons provide reference points for researchers and policy analysts to understand trends and patterns in national education data and are important as U.S. students compete in an increasingly global economy.
Education at a Glance, an annual publication produced by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), provides data on the structure, finances, and performance of education systems in 38 OECD countries, including the United States, as well as a number of OECD partner countries. The report also includes state-level information on key benchmarks to inform state and local policies on global competitiveness.
The recently released 2021 edition of the report shows that the United States is above the international average on some measures, such as participation in and funding of postsecondary education, but lags behind in others, such as participation in early childhood education programs. The report also presents some initial comparisons on countries’ responses to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Postsecondary Educational Attainment
The percentage of U.S. 25- to 34-year-olds with a postsecondary degree increased by 10 percentage points between 2010 and 2020, reaching 52 percent, compared with the OECD average of 45 percent (figure 1). Attainment rates varied widely across the United States in 2020, from 33 percent for those living in Nevada to 61 percent for those living in Massachusetts and 77 percent for those living in the District of Columbia.
Figure 1. Percentage of 25- to 34-year-olds with a postsecondary degree, by Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) country: 2020
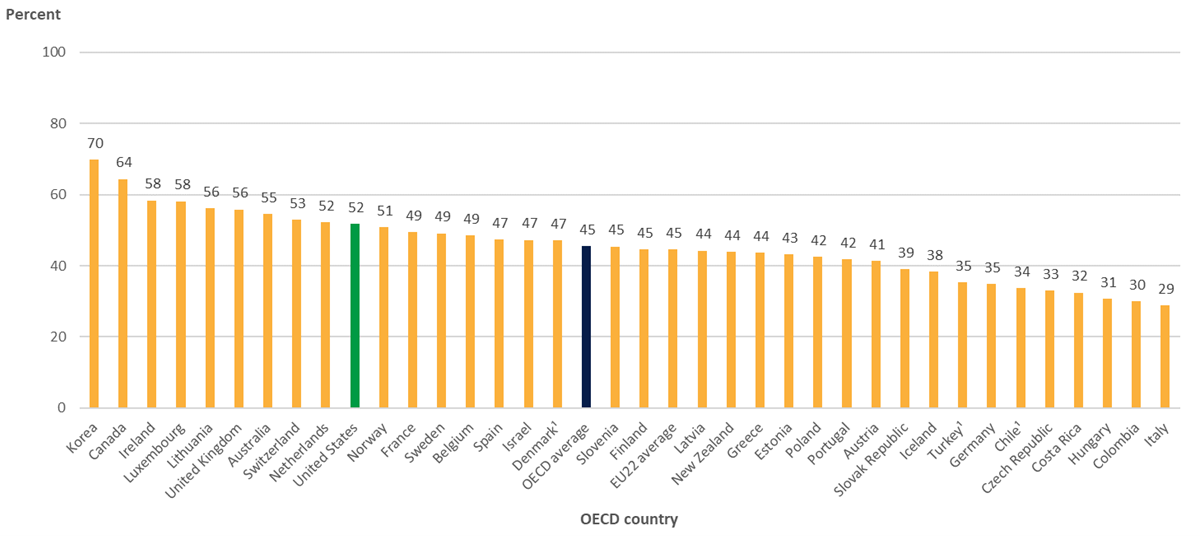
1 Year of reference differs from 2020. Refer to the source table for more details.
SOURCE: OECD (2021), Table A1.2. See Source section for more information and Annex 3 for notes.
In the United States in 2020, 25- to 34-year-old women were more likely than 25- to 34-year-old men to attain a postsecondary education: 57 percent of women had a postsecondary qualification, compared with 47 percent of men, a difference of 10 percentage points. Across OECD countries, the postsecondary education gap between 25- to 34-year-old men and women was wider (13 percentage points) than the gap in the United States (10 percentage points). In 2020, the postsecondary attainment rate of 25- to 34-year-old men in the United States was 8 percentage points higher than the OECD average, whereas the rate of 25- to 34-year-old women in the United States was 5 percentage points higher than the OECD average.
Postsecondary Education Spending
U.S. spending on postsecondary education is also relatively high compared with the OECD average, in both absolute and relative terms. The United States spent $34,036 per postsecondary student in 2018, the second-highest amount after Luxembourg and nearly double the OECD average ($17,065). Also, U.S. spending on postsecondary education as a percentage of GDP (2.5 percent) was substantially higher than the OECD average (1.4 percent). These total expenditures include amounts received from governments, students, and all other sources.
Early Childhood Education
The level of participation in early childhood education programs in the United States is below the OECD average and falling further behind. Between 2005 and 2019, average enrollment rates for 3- to 5-year-olds across OECD countries increased from 77 to 87 percent. In contrast, the rate in the United States remained stable at 66 percent during this time period. Among U.S. states, the 2019 enrollment rates for 3- to 5-year-olds ranged from less than 50 percent in Idaho and North Dakota to 70 percent or more in New York (70 percent), Vermont (76 percent), Connecticut (76 percent), New Jersey (77 percent), and the District of Columbia (88 percent).
COVID-19 Pandemic
Education at a Glance also presents a first look at countries’ responses to the COVID-19 pandemic. The spread of COVID-19 impeded access to in-person education in many countries around the world in 2020 and 2021. By mid-May 2021, 37 OECD and partner countries had experienced periods of full school closure since the start of 2020.
Despite the impact of the crisis on employment, the share of NEETs (those neither in employment nor education or training) among 18- to 24-year-olds did not greatly increase in most OECD and partner countries during the first year of the COVID-19 crisis. On average, the share of 18- to 24-year-old NEETs in OECD countries rose from 14.4 percent in 2019 to 16.1 percent in 2020. However, Canada, Columbia, and the United States experienced an increase of more than 4 percentage points. In the United States, the share of 18- to 24-year-old NEETs increased from 14.6 percent in 2019 to 19.3 percent in 2020.
In 2020, many postsecondary education institutions around the world closed down to control the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, potentially affecting more than 3.9 million international and foreign students studying in OECD countries. Early estimates show the percentage of international students attending postsecondary institutions in the United States declined by 16 percent between 2020 and 2021.
Browse the full report to see how the United States compares with other countries on these and other important education-related topics and learn more about how other countries’ education systems responded to the COVID-19 pandemic.
By Rachel Dinkes, AIR