
Reciprocal teaching was found to have mixed effects on comprehension for adolescent learners.
A group of closely related outcomes.
A summary of the effectiveness of an intervention in an outcome domain, based on the quality of research, the statistical significance of findings, the magnitude of findings, and the consistency of findings across studies.
Positive: strong evidence that intervention had a positive effect on outcomes. |
Potentially Positive: evidence that intervention had a positive effect on outcomes with no overriding contrary evidence. |
Mixed: evidence that intervention’s effect on outcomes is inconsistent. |
No Discernible: no evidence that intervention had an effect on outcomes. |
Potentially Negative: evidence that intervention had a negative effect on outcomes with no overriding contrary evidence. |
Negative: strong evidence that intervention had a negative effect on outcomes. |
For more, please see the WWC Glossary entry for rating of effectiveness.
Evidence Tier
The Department of Education’s evidence tiers. For more information, please see the WWC Glossary entry for evidence tiers.
The percent of each characteristic is based on the sample size of all studies meeting standards that reported data on the characteristic.
Percentages below may not add to 100 percent.
|
Outcome domain |
Effectiveness Rating | Grades | Evidence Tier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comprehension | 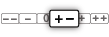 |
4-12 |

|
Last Updated: September 2010
Race
| Asian | 81% | |
| Native American | 19% | |
| Pacific Islander | 14% |
Ethnicity
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 100% |
Gender
Free & Reduced-Price Lunch
Delivery Method
Urbanicity
Locations
This intervention report was prepared for the WWC by Mathematica under contract ED-07-CO-0062.