The Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS) is a comprehensive federal data source that collects information on key features of higher education in the United States, including characteristics of postsecondary institutions, college student enrollment and academic outcomes, and institutions’ employees and finances, among other topics.
The National Center for Education Statistics (NCES) has created a new resource page, Student Cohorts and Subgroups in IPEDS, that provides data reporters and users an overview of how IPEDS collects information related to postsecondary students and staff. This blog post highlights key takeaways from the resource page.
IPEDS survey components collect counts of key student and staff subgroups of interest to the higher education community.
Data users—including researchers, policy analysts, and prospective college students—may be interested in particular demographic groups within U.S. higher education. IPEDS captures data on a range of student and staff subgroups, including race/ethnicity, gender, age categories, Federal Pell Grant recipient status, transfer-in status, and part-time enrollment status.
The Outcome Measures (OM) survey component stands out as an example of how IPEDS collects student subgroups that are of interest to the higher education community. Within this survey component, all entering degree/certificate-seeking undergraduates are divided into one of eight subgroups by entering status (i.e., first-time or non-first-time), attendance status (i.e., full-time or part-time), and Pell Grant recipient status.
Although IPEDS is not a student-level data system, many of its survey components collect counts of students and staff by subgroup.
Many IPEDS survey components—such as Admissions, Fall Enrollment, and Human Resources—collect data as counts of individuals (i.e., students or staff) by subgroup (e.g., race/ethnicity, gender) (exhibit 1). Other IPEDS survey components—such as Graduation Rates, Graduation Rates 200%, and Outcome Measures—also include selected student subgroups but monitor cohorts of entering degree/certificate-seeking students over time to document their long-term completion and enrollment outcomes. A cohort is a specific group of students established for tracking purposes. The cohort year is based on the year that a cohort of students begins attending college.
Exhibit 1. IPEDS survey components that collect counts of individuals by subgroup
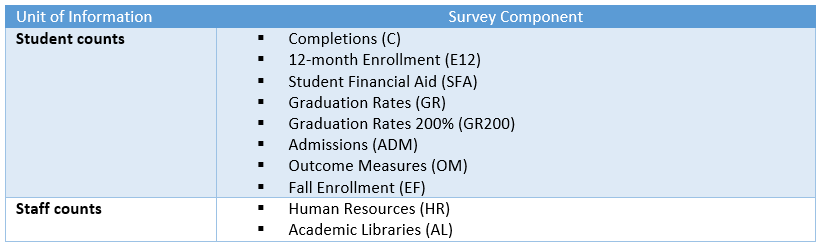
IPEDS collects student and staff counts by combinations of interacting subgroups.
For survey components that collect student or staff counts, individuals are often reported in disaggregated demographic groups, which allows for more detailed understanding of specific subpopulations. For example, the Fall Enrollment (EF) and 12-month Enrollment (E12) survey components collect total undergraduate enrollment counts disaggregated by all possible combinations of students’ full- or part-time status, gender, degree/certificate-seeking status, and race/ethnicity. Exhibit 2 provides an excerpt of the EF survey component’s primary data collection screen (Part A), in which data reporters provide counts of students who fall within each demographic group indicated by the blank cells.
Exhibit 2. Excerpt of IPEDS Fall Enrollment (EF) survey component data collection screen for full-time undergraduate men: 2022–23
[click image to enlarge]
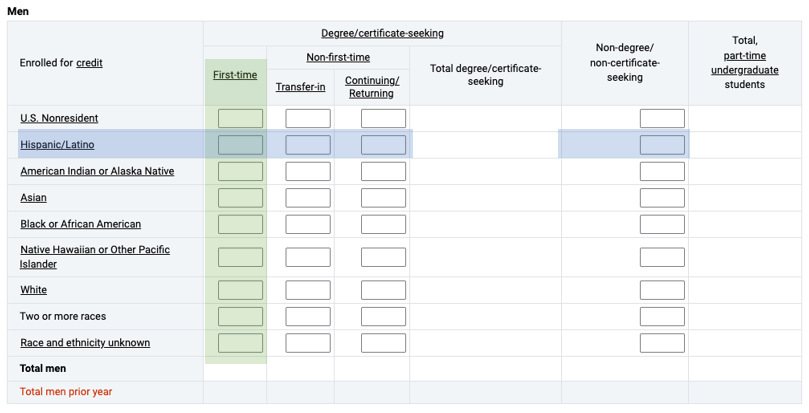
NOTE: This exhibit reflects the primary data collection screen (Part A) for the 2022–23 Fall Enrollment (EF) survey component for full-time undergraduate men. This screen is duplicated three more times for undergraduate students, once each for part-time men, full-time women, and part-time women. For survey materials for all 12 IPEDS survey components, including complete data collection forms and detailed reporting instructions, visit the IPEDS Survey Materials website.
As IPEDS does not collect data at the individual student level, these combinations of interacting subgroups are the smallest unit of information available in IPEDS. However, data users may wish to aggregate these smaller subgroups to arrive at larger groups that reflect broader populations of interest.
For example, using the information presented in exhibit 2, a data user could sum all the values highlighted in the green column to arrive at the total enrollment count of full-time, first-time men. As another example, a data user could sum all the values highlighted in the blue row to determine the total enrollment count of full-time Hispanic/Latino men. Note, however, that many IPEDS data products provide precalculated aggregated values (e.g., total undergraduate enrollment), but data are collected at these smaller units of information (i.e., disaggregated subgroup categories).
Student enrollment counts and cohorts align across IPEDS survey components.
There are several instances when student enrollment or cohort counts reported in one survey component should match or very closely mirror those same counts reported in another survey component. For example, the number of first-time degree/certificate-seeking undergraduate students in a particular fall term should be consistently reported in the Admissions (ADM) and Fall Enrollment (EF) survey components within the same data collection year (see letter A in exhibit 3).
Exhibit 3. Alignment of enrollment counts and cohorts across IPEDS survey components
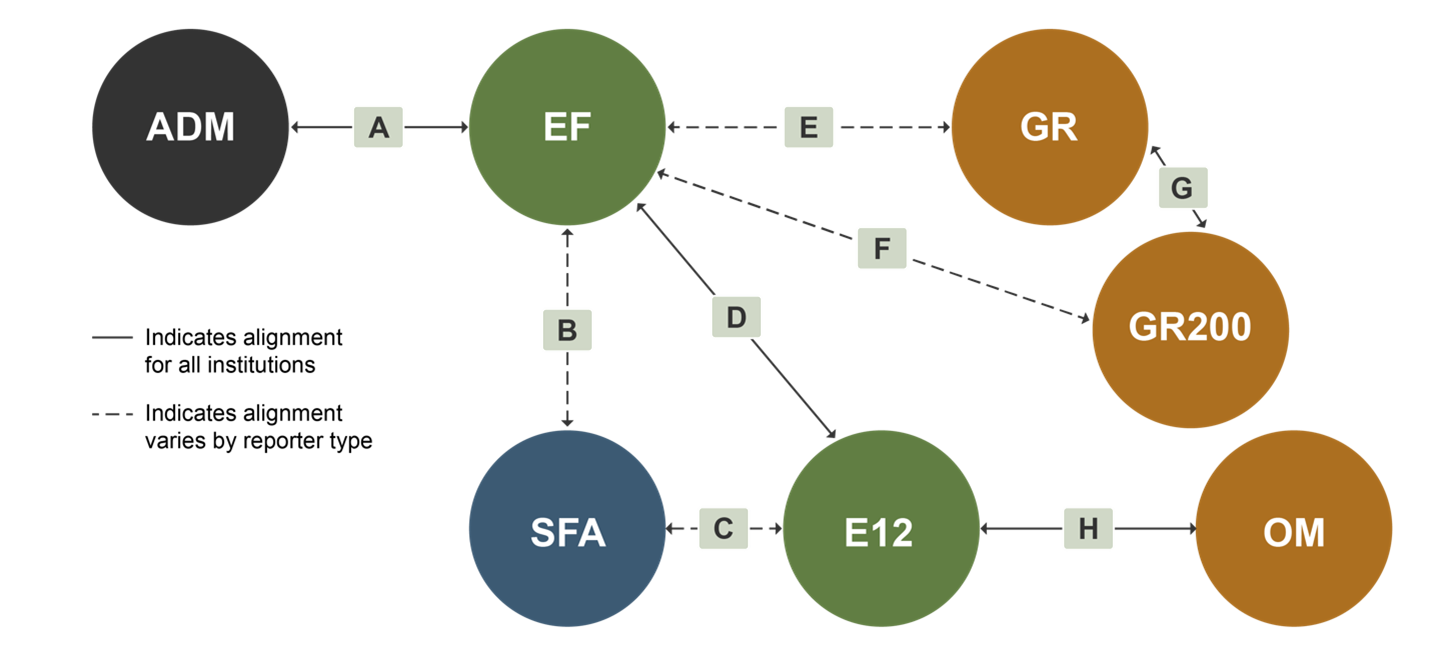
For a full explanation of the alignment of student counts and cohorts across IPEDS survey components (letters A to H in exhibit 3), visit the Student Cohorts and Subgroups in IPEDS resource page.
Be sure to follow NCES on Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and YouTube, follow IPEDS on Twitter, and subscribe to the NCES News Flash to stay up-to-date on IPEDS data releases and resources.
By Katie Hyland and Roman Ruiz, AIR